
WIlliam B. Norton is a consultant, author of The Internet Peering Playbook: Connecting to the Core of the Internet, and highly sought after public speaker and international recognized expert on Internet Peering. He is currently engaged as the Executive Director and Consultant for DrPeering.net, a leading Internet Peering portal and consultancy. With over twenty years of experience, Mr. Norton focuses his attention on sharing his knowledge with the broader community in the form of presentations, Internet white papers, and private on-site consultations.
From 1998-2008, Mr. Norton’s title was Co-Founder and Chief Technical Liaison for Equinix, a leading Internet Peering Exchange and colocation center provider. From startup to IPO and until 2008 when the market cap for Equinix was $3.6B, Mr. Norton spent 90% of his time working closely with the Peering Coordinator Community. As an established thought leader, his focus was on building a critical mass of carriers, ISPs and Content Providers and documenting the core values that Internet Peering provided, including the Peering Break Even Point and Estimating the Value of an Internet Exchange.
To this end, he created the white paper process, identifying interesting and important Internet Peering operations topics, and documenting what he learned from the peering community. He published and presented his research white papers in over 100 international operations and research forums. These activities helped establish the relationships necessary to attract the set of Tier 1 ISPs, Tier 2 ISPs, Cable Companies, and Content Providers necessary for a healthy Internet Exchange Point ecosystem.
Mr. Norton developed the first business plan for the North American Network Operator's Group (NANOG), the Operations forum for the North American Internet. He was chair of NANOG from May 1995 to June 1998 and was elected to the first NANOG Steering Committee post-NANOG revolution.
William B. Norton received his Computer Science degree from State University of New York Potsdam in 1986 and his MBA from the Michigan Business School in 1998.
Connect on-line: http://DrPeering.net – RSS: http://ask.DrPeering.net – e-mail: wbn@TheCoreOfTheInter.net
To help people select which white papers to read, we have marked them according to how much background knowledge the reader is assumed to have.
| No advanced knowledge of Internet Peering is needed to understand this document. | |
| Some advanced knowledge of Internet Peering is assumed. | |
| This white paper may be difficult to fully understand without background knowledge of the Internet Peering field. | |
Some Internet Exchange Point Operators have told DrPeering that they point their engineering and sales folks to these white papers and suggest that they start out with the ![]() white papers, migrate to the
white papers, migrate to the ![]() white papers, and finish with the
white papers, and finish with the ![]() white papers when they have some working experience with peering. This seems to help so we kept the convention going. One can also peruse these documents by looking to the tutorials sequences on the home page.
white papers when they have some working experience with peering. This seems to help so we kept the convention going. One can also peruse these documents by looking to the tutorials sequences on the home page.
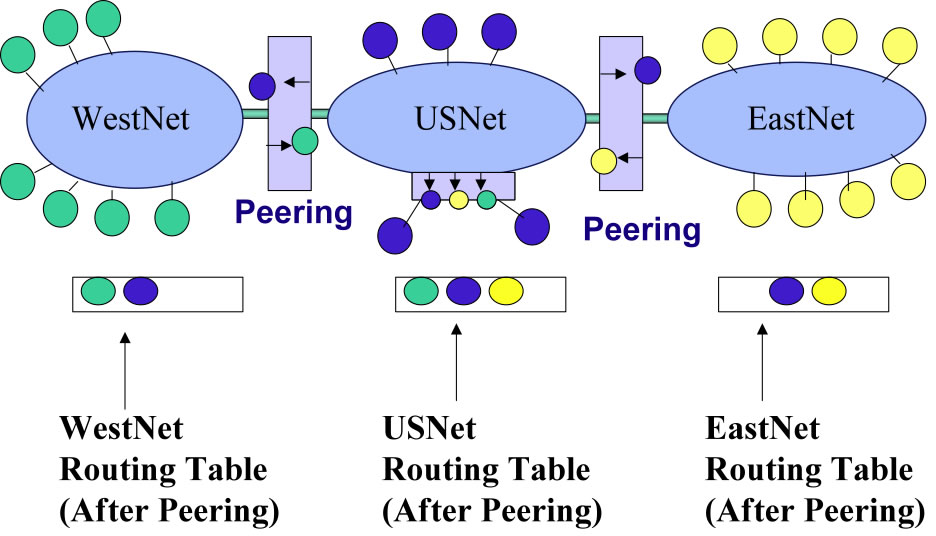
This white paper focuses on the definitions and processes of peering. It identifies the 9 selection criteria ISPs told me that they use to determine which IX to build into as well. This one is in use in networking classes at Universities across the US! I would recommend this one and A Business Case for Peering for folks just getting into peering. More advanced and more technical folks would be interested in The Art of Peering: The Peering Playbook, as it deals with more strategic "Tricks of the Trade".
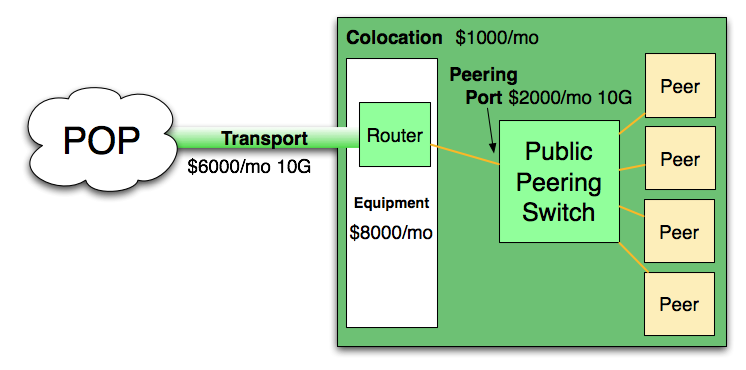
The Business Case for Peering White Paper is intended for the CFO who just wants the economic argument for peering, specifically, "Why should I spend money on something that won't generate any revenue?" There is after all a cost of peering (transport to an IX, rack and port fees, and equipment costs) and the CFO just wants to be shown the break even point where peering makes sense. Rewritten for 2010 applying market pricing.
This brief provides the data showing that Internet Transit has declined in price an average of 61% each year from 1998 to 2010. We share the data, the graph and the spreadsheet so others can make use of the data. This is one of the most requested pages on the site.
Introductory Peering White Papers - Start Here
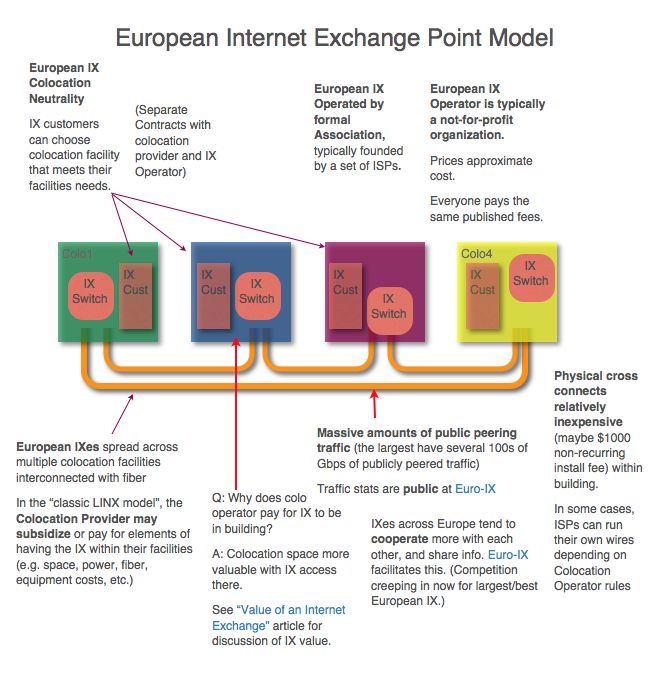
How is peering different in the U.S. vs in Europe? There are some differences in how IXes were set up and continue to run as compared with the U.S. version. This article explores these differences.
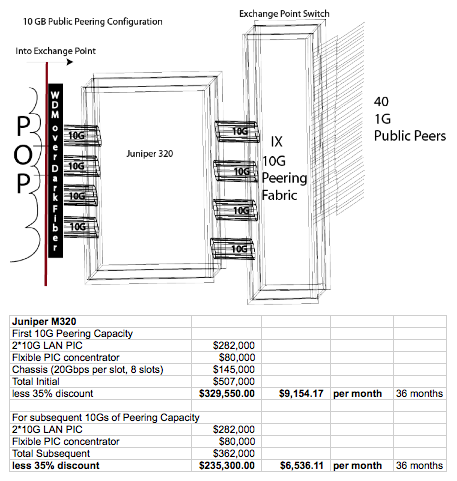
The Public vs. Private peering debate part is required because the Peering Coordinator Community points out that the next best alternative to 10G public peering is peeling off cross connects or circuits for private peering, so the paper compares these two options.
DrPeering reviewed 28 Internet Peering Policies to examine the language used in peering policies, to see if one could categorize common peering policy clauses. As it turns out, many of the peering policy clauses were very similar if not identical. We placed these clauses into categories, each with their own web page so the community can compare the wording of their favorite peering policy clauses.
This has proven invaluable for training and for those looking to design their own peering policy.
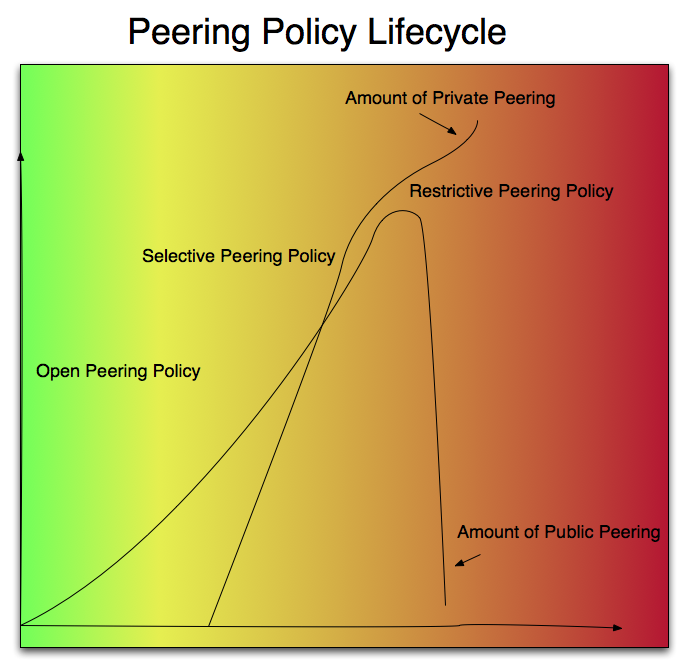
This early draft documents a position first articulated by Vijay Gill that peering policies tend to go through a life cycle as companies grow and eventually get to Tier 1 ISP status.
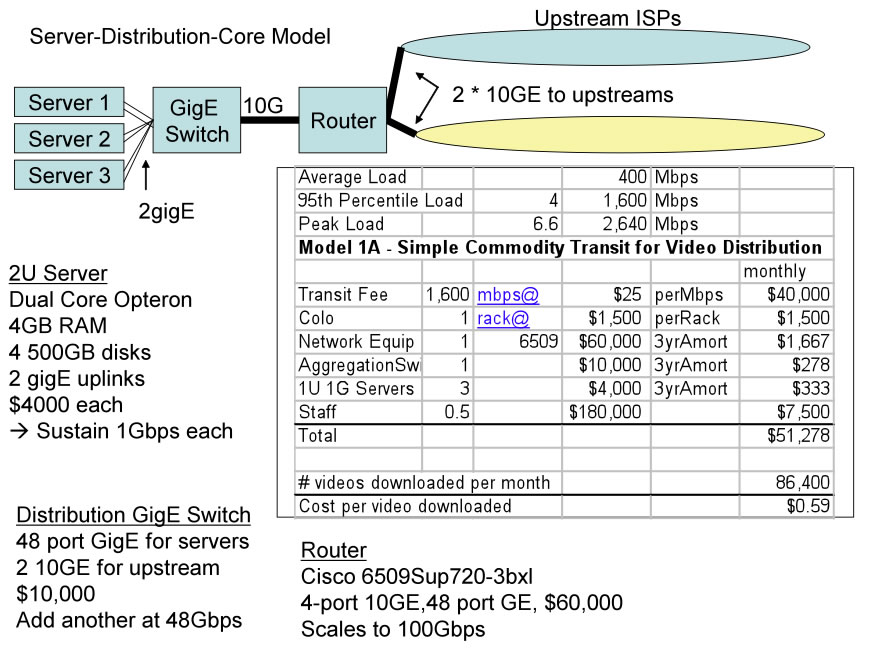
In previous research we documented three significant disruptions to the U.S. Peering Ecosystem as the Cable Companies, Large Scale Network Savvy Content Companies, and Tier 2 ISPs started peering openly. By peering content directly with eyeballs, they effectively bypassed the Tier 1 ISPs resulting in improved performance, greater control over the end- user experience, and overall lower operating costs.
This paper predicts a new wave of disruption that potentially dwarfs this previous redirection of Internet traffic. Short video clip web sites, full length motion pictures, and television shows are now available via streaming to on-line devices and via downloading to iPods. High quality movies from independent producers are being distributed via peer-to-peer methods. We observe these flash crowd effects and the larger movie file sizes as the crest of the first wave of significant incremental load on the Internet.
The majority of this paper details four models for Internet Video Distribution (Transit, Content Delivery Networks, Transit/Peering/DIY CDN, Peer-to-peer) across three load models. The cost models include network and server equipment along with pricing models for various distribution methods. Over one hundred walkthroughs of this paper have led to stepwise refinements of the models and insights into why one would prefer or not prefer one model over the other.
The summary of the paper is a comparison of these video distribution techniques in terms of $-per-video units from the Video Service Provider perspective. We highlight cascading obstacles preventing large scale delivery of video traffic using commodity transit in a single location. The CDN solution and the multi-site Transit with Peering solution bypass some of these obstacles, while the peer-to-peer solution, while controversial, yields (by far) the lowest cost solution from the video service provider perspective.
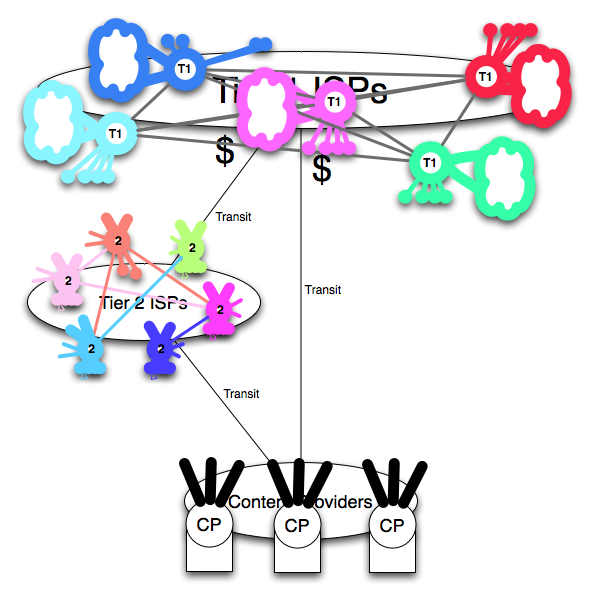
This white paper documents the new U.S. Peering Ecosystem that emerged from the ashes of the telecom collapse in 2000-2002. Peering changed dramatically as the Cable companies, large network-savvy content players got into peering in a big way. This is best suited to broadband and large content providers who want to see if peering fits. They will see the leaders in the industry going down the peering path and saving significant money (>$1 million per annum).
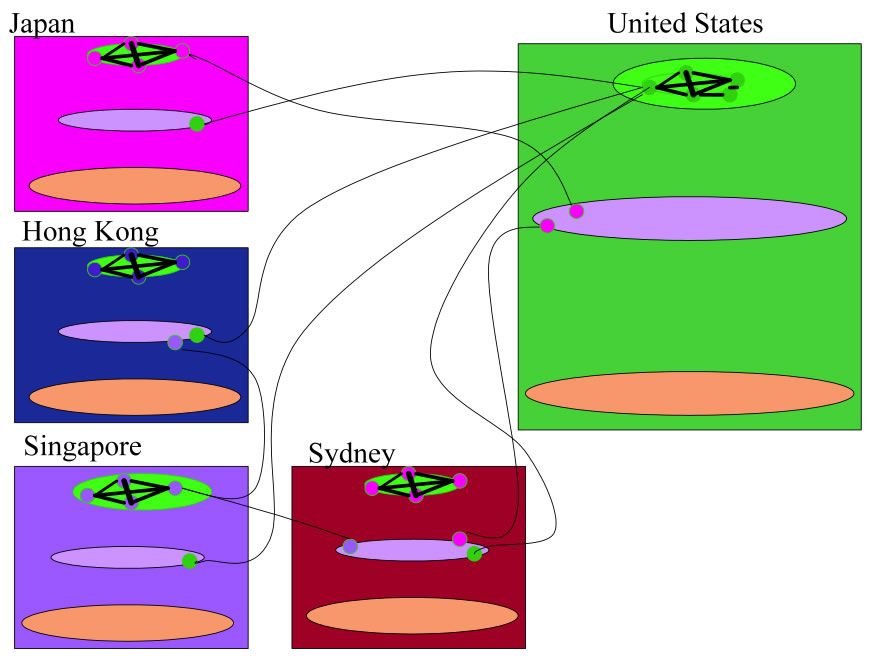
This is the latest white paper focusing on the things that Peering Coordinators said they wished they had known before building into Asia. It identifies 5 reasons to build into Asia, 4 International Interconnection Strategies 1 peering dynamic that may seem counter intuitive, along with 9 "lessons learned." The second half of the paper identifies specific characteristics of the Japan, Hong Kong, Singapore and Australia Peering Ecosystems.
This white paper is most appropriate for those who are exploring expanding into Asia. As the newest, this white paper is still in early draft stage and about to be circulated for broader comments so expect it to be updated several times over the next few months.
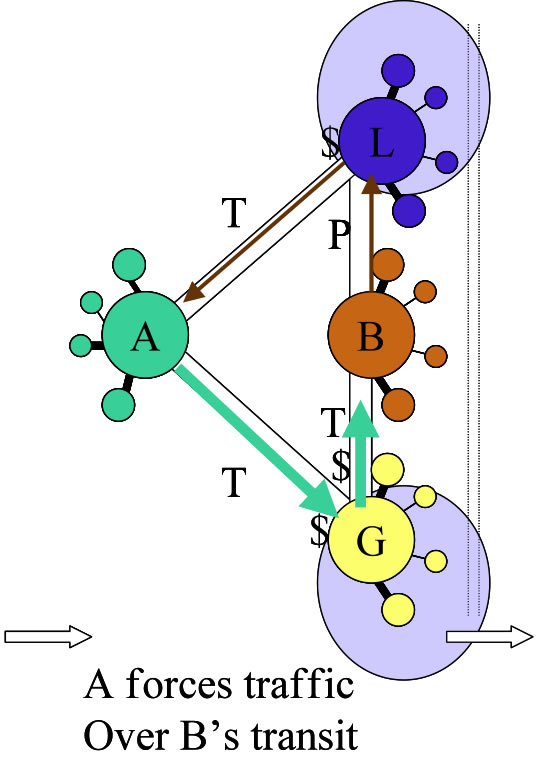
This is the most controversial peering white paper as it identifies the peering "Tricks of the Trade", those tactics that Peering Coordinators have shared with me that have successfully been used to obtain peering where they otherwise would not have been able to. It is controversial because some of the tactics are ethically questionable - to be listed, the only requirement was that the tactics had to have been successfully used to obtain peering where they otherwise would not have been able to. This paper is best suited to advanced peering coordinators, those having difficulty obtaining peering (content-heavy ISPs and content players), and technical folks interested in seeing how routing is strategically applied to achieve strategic peering & business goals.
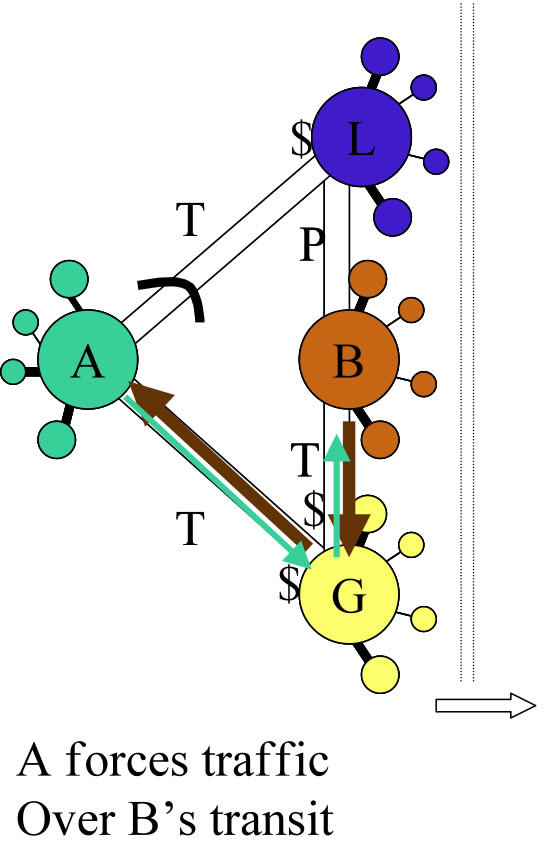
Does it make sense to use Peering Traffic Ratios to determine if a peering partner will work for you?
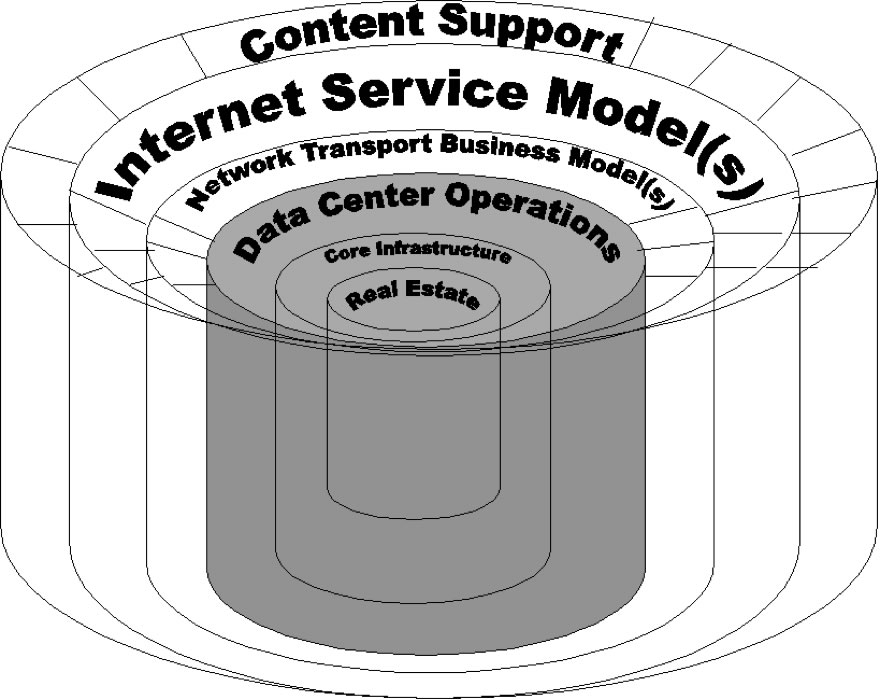
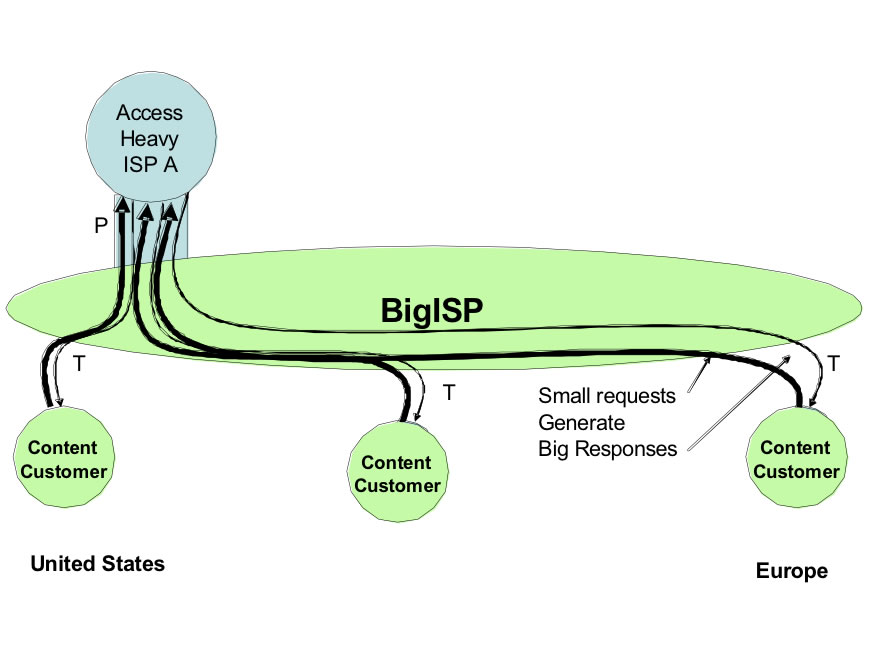
This paper explores the trade-offs between building a data center and outsourcing the data center to a third party. The scope of this research is limited to the common "core infrastructure", that is, the systems that all Internet data centers require regardless of business model. We will explicitly not be discussing web design, construction, hosting, monitoring, or management and operations services. These activities are required regardless of whether or not the Internet data center is outsourced or not. We are focusing this research solely on the decision rule: when does it make sense to build your own data center and when does it make sense to outsource it?
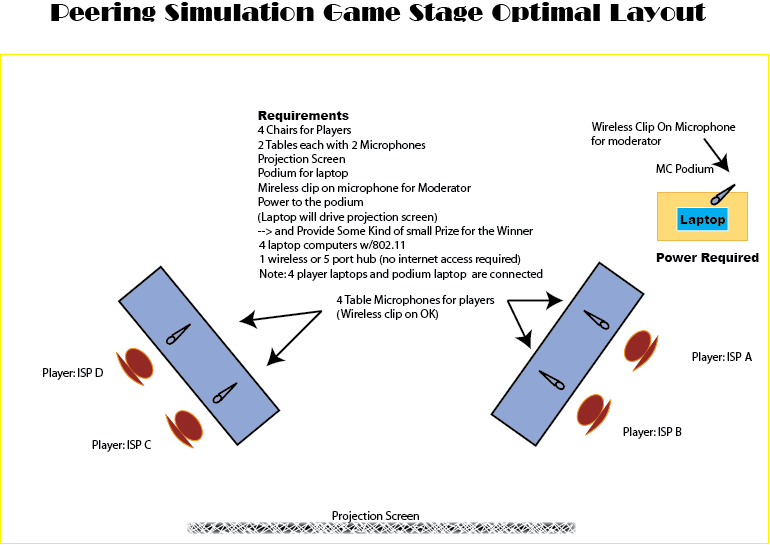
The Peering Simulation Game is based upon the research ("Internet Service Providers and Peering" and "A Business Case for Peering") that documents ISP peering practices, motivations, and strategies, and was designed to demonstrate ISP peering negotiations through a live simulation. In this simulation, four audience members play the role of ISP Peering Coordinator, rolling the dice and growing their network by acquiring customer "squares" on a virtual game board. They receive money for each square they occupy but must pay transit fees to their upstream ISP to access the rest of the "Internet". By negotiating peering, the Peering Coordinators reduce their transit costs. The goal of the game is to maximize their bank account. Since the ISPs both cooperate in peering to reduce costs and compete to maximize their bank accounts, this game has proven to bring forward peering negotiations strikingly similar to peering negotiations in the real world.
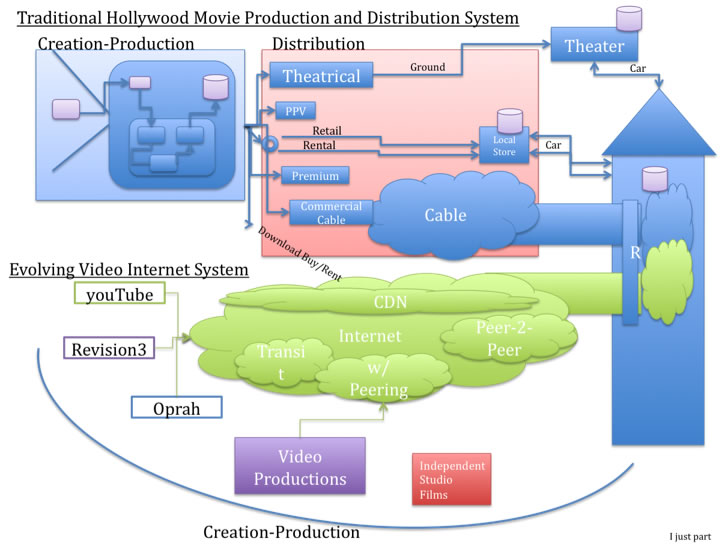
In this brief we share some initial insights into the migration of video traffic from traditional channels into what can best be described as an emerging Video Internet Ecosystem video or presentation recorded at NZNOG 2010.
Two ecosystems have evolved to delivery video to consumers: the Hollywood system, based on over one hundred years of evolution, and the Video Internet System, based on only ten years of evolution. These ecosystems are mostly parallel but in some places interconnect, clash, converge and rapidly evolve. One thing in common to both is that innovations are fundamentally changing the viewer experience. We will compare these two systems at a high level, highlight how they work and highlight some potential trajectories..
In this paper we brief the reader on the North American Network Operator's Group (NANOG), what led up to it and the early days of operating the forum. This is useful for those anticipating setting up a regional network operator's group (there have been many *NOG organizations since the launch of NANOG.
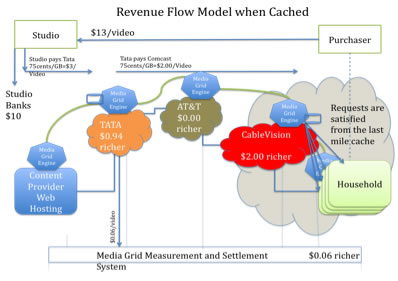
This controversial paper is a starting point for an entire business model ecosystem designed to distribute of latency and loss sensitive Internet objects. For a set of premium content producers, there is a willingness to pay a little more for a guaranteed high-quality end-user experience. For some Internet Service Providers, there is a willingness to expend resources if there is a corresponding increase in revenue. What is needed is an ecosystem that supports both of these goals.
An overlay network called a "Media Grid" is introduced in this paper. A revenue allocation model is introduced along with two scenarios; before caching, and when the object is served entirely out of last mile cache. These scenarios are discussed with the goal of aligning the interests of all of those participating in the cooperatively managed video delivery ecosystem.
Related to this work is the informal study "The Top 10 Reasons QoS hasn't taken off" shared at a private workshop as a power point presentation.
This work was funded in part by nuMetra and the InterStream Association in 2009.
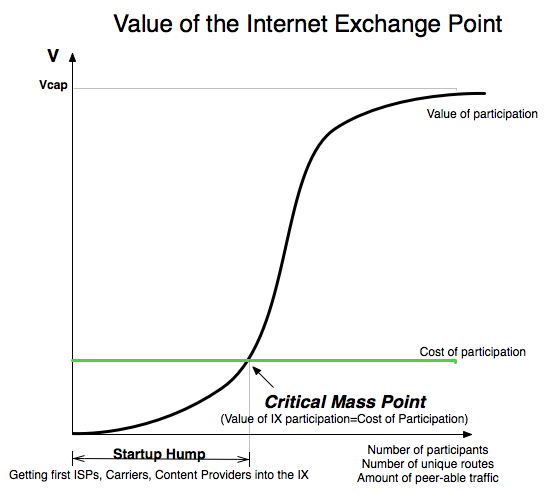
This is the follow on to the Art of Peering : The Peering Playbook, but intended for emerging Internet Exchange Point Operators. It highlights the tricks of the trade - "How does an IX get to critical mass?" We highlight a dozen approaches that have been used and discuss the pro's and con's of each
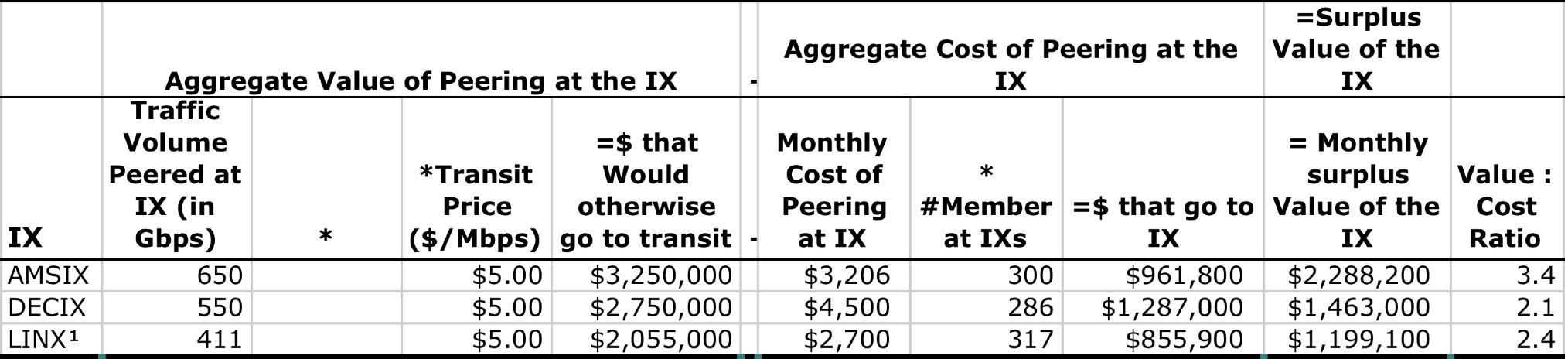
In this white paper we model an Internet Exchange Point from the perspective of an IX customer to answer the question - what is the financial value of an Internet Exchange Point to its population?"
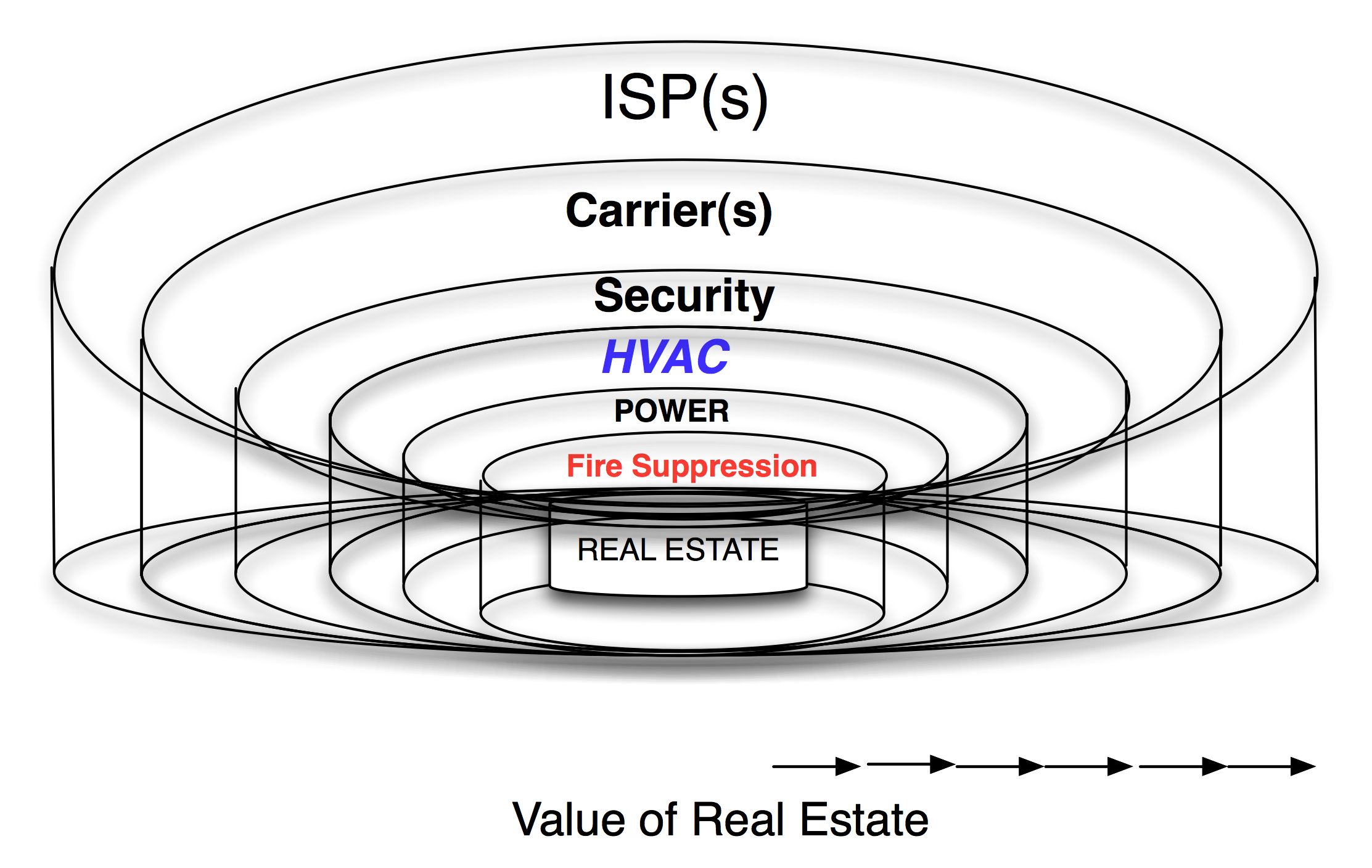
In this white paper answer the question - "Is Colocation just high priced real estate?". As it turns out there is a real art to building and maintaining the right mix of participants that participate in a complex ecosystem.

Most IXes have a person who acts as a Chief Technical Liaison but without the title - you should get to know these people who know everyone. You may recognize the person after you read what the person actually does.
This brief documents the top selection criteria ISPs said they use to choose which Internet Exchange Point to build into.
This legacy white paper was the first to address the trade-offs between using exchange points or point to point circuits. It presents a proof that if there are more than 5 parties seeking interconnection, a central place with fiber between them wins big.
This describes the Peering Personals events, a little bit about the Peering Coordinator Community anf how to break into the Peering Community.




Jay Adelson, Al Avery, Bill Norton - Early Equinix Photos - 1998
In early 1998, Jay Adelson and Al Avery were interested in expanding the PAIX model internationally. DEC, the owner of the PAIX at the time, was not enthusiastic about the plan. So Jay and Al left the PAIX and contacted me in June about being on their Technical Advisory Board (TAB). I mentioned that I just graduated with my MBA from the Michigan Business School and that, since I was studying entrepreneurship for the last bunch of years, maybe I could help them launch this new venture. They agreed and I was brought in as Co-Founder and Director of Business Development, a title later upgraded to Co-Founder and Chief Technical Liaison which was somewhat more reflective of what I did on a daily basis.
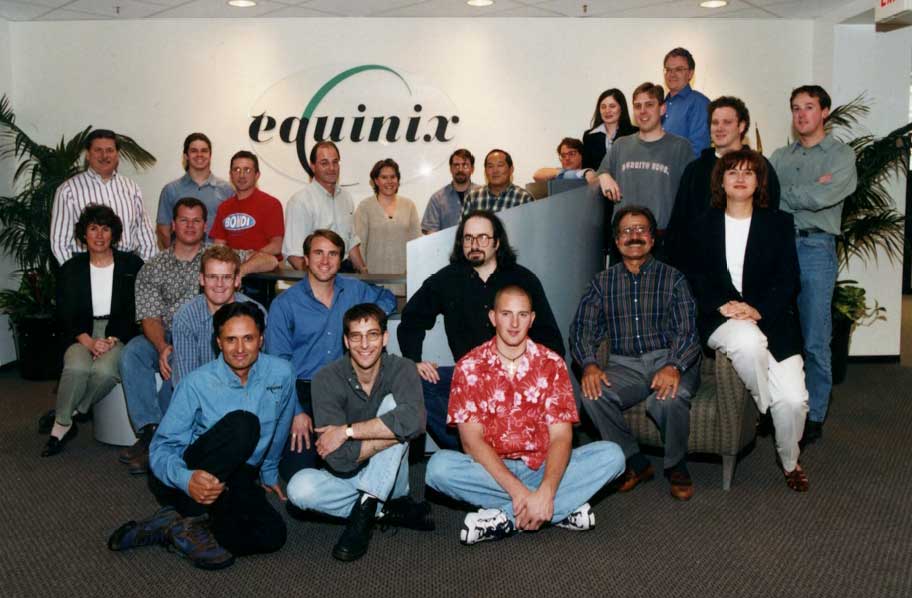

Early Equinix photo. Logo was just delivered to the front desk. Some names I remember include Greg McHugh, Dan Gisi, Keith Taylor, Kumar ___, Jay Adelson, Bill Norton, Lisa Luciana, Matt Wood, Art _____, Jeff Rizzo, Ted Hardie, Atam Lachandani (sp?), Al Avery, Dermott (sp?)
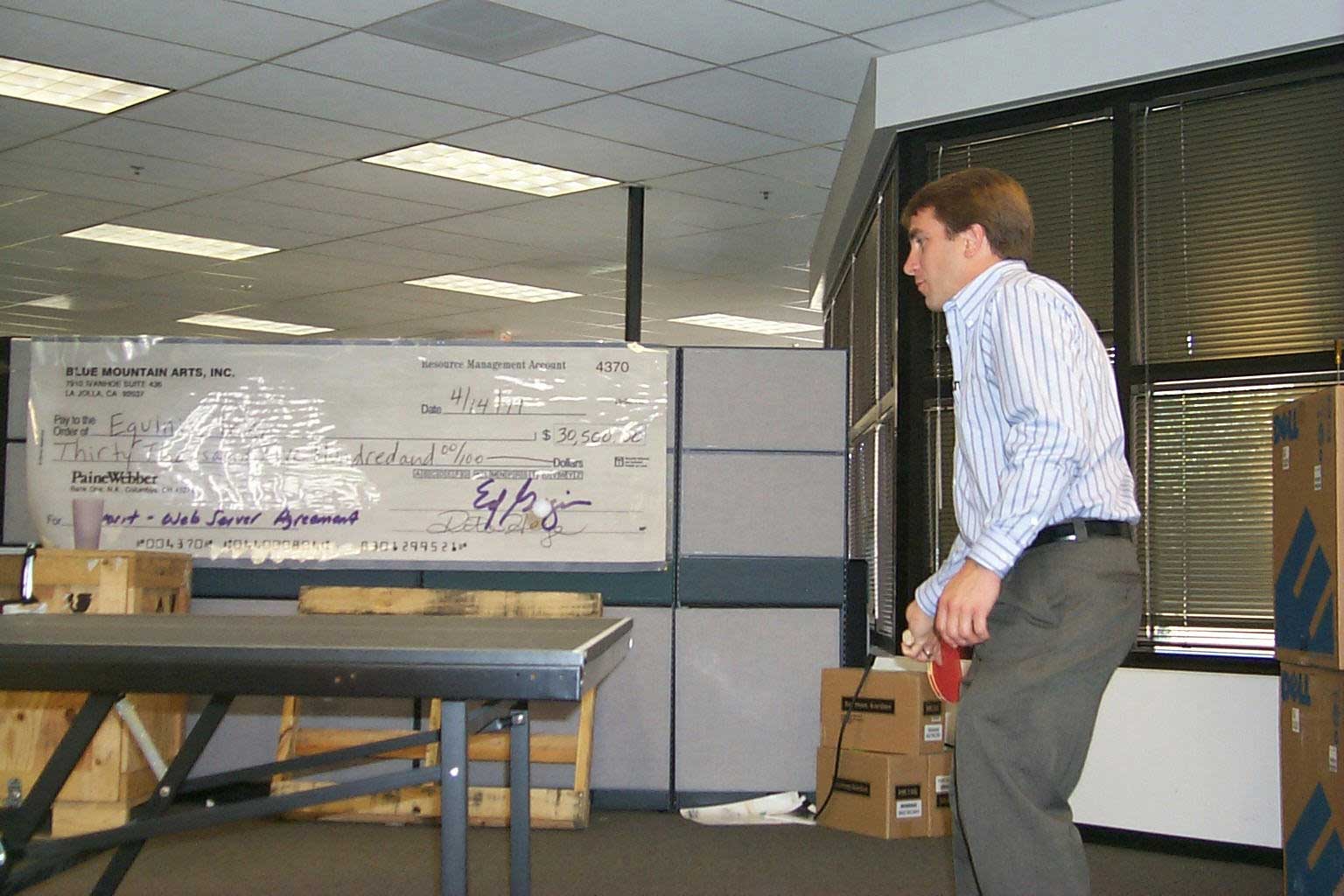

Bill Norton playing ping pong in front of the first revenue Equinix received
I was successful in bringing in the first Equinix customer, Blue Mountain Arts - see the check in the background in the picture above. I brought in Yahoo!, at the time, Equinix's largest and most prominant customer, and helped bring in the Tier 1 ISPs, the Cable Companies, and some of the largest international ISPs in the world. It was during these first few years that 95% of the heavy lifting was done in my opinion. I credit the early sales team with much of the success here. Beyond that point, the value of the IX was there and it became a much easier sale.

Martin Levy, Bill Norton, Avi Freedman, Brokaw Price
From the beginning I was travelling all the time - I was 90% externally focused. As Jay and Al were building out the team, hiring like crazy and build the IBXes, I was speaking at conferences, doing market research, trying to understand and document if and when Internet Exchange Points made sense from the customer point of view. I shared everything I learned back to the community in the form of Internet White Papers.
I believe much of my success was from the travel - the relationships established and maintained, the business cases I helped build for the community and the individual companies, the white papers made freely available, the leadership demonstrated chairing NANOG, running the early Equinix GPFs, the NANOG Peering BOFs and APRICOT Peering Tracks.
One thing I heard loud and clear from all of these customer contacts was that it wasn't about the data centers - people said "Bill, I expect you are going to keep the lights on and the building cool. What else do you have?"

Touring the old paper facility that became the Chicago IBX
It was about the ecosystems, the revenue that would be made by participating in the Internet Exchanges, and the cost savings resulting by peering.
Image from one of many wbn white papers detailing the practice of Internet Peering.
In retrospect, I took quite a gamble. I sold my home in Michigan and everything I owned to come out to Silicon Valley, the home of the startup ! After eleven years at a not-for-profit watching all my NANOG friends getting rich, finally it was my turn to roll ! During my 10 years at Equinix (1998-2008) we went from the startup phase through the IPO, into and through a painful economic downturn and recovery. After my stock options finished vesting in April 2008 I left Equinix with a market cap of $3.6B. What a ride!

Bill Norton accepting award at Web Hosting event.
From 2008 on I worked on DrPeering.net, an iPhone web App for LocalCook.com and also provided some part-time consulting for too many companies to mention. I find this work very rewarding so I continue to help startups launch, and now survive and thrive in these difficult times.

The subset of Internet Data Centers and Internet Exchange Environments I have toured:
| Percentage of Time | Activity |
|---|---|
| 50% | Client Engagements and Workshops |
| 20% | Administration |
| 10% | Professional Development |
| 10% | Pro Bono - talks at colleges and local events, travel costs covered remote speaking engagements with business class for international engagements (African Interconnection Conference for example), NANOG Finance Workgroup, etc. |
| 10% | Community Service - YMCA Board of Directors work, fundraising, for example |
William B. Norton - Sample Introduction text for speaking events
Our next speaker brings over 20 years of Internet Peering expertise to the forum.
Bill Norton worked on the NSFNET project which operated the core of the pre-commercial Internet.
He chaired the North American Network Operators Group (NANOG), the operations forum for the north american Internet.
And he was Co-Founder and Chief Technical Liaison for Equinix, a large scale commercial Internet Exchange Point operator. After 10 years at Equinix, Mr Norton retired and launched Dr Peering International, a peering consultancy. He is the author of The Internet Peering Plaubook, which remains the world's only book devoted to the practice of Internet Peering.
Please welcome Bill Norton.